The problem of Poverty
Definition of poverty is an arbitrary task
In the United States, the poverty threshold is the minimum income required to purchase the necessities of life
Those that fall below this threshold would be considered poor
In 2009 for an adult living alone the figure was at $10,956; for two adults and two children, it was at $21,756
Poverty rates fell steeply in the 1960s down to between 10-15% in the 1970s. But, despite increased prosperity, the numbers have stayed relatively stagnant
Who are the Poor?
In 2009 (according to the US Census Bureau), 43.5 million Americans were in poverty, or roughly 4.3% of the population, or 1 in 7 people
25.9% of African-Americans and 25.3% of Hispanics were considered poor. 9.4% of non-Hispanic whites below the poverty threshold
Female-headed households had a poverty rate of 32.5% while married couples had a relatively smaller poverty rate of 5.8%
Many part-time workers consist of a category analysts refer to as the working poor, usually because part-time work does not include health benefits, retirement or paid vacation
What Causes Poverty
Lack of education is the primary culprit in poverty
In 1979 the average hourly wage of a man with a college education was 36% higher than a man with a high school diploma
In 2009 this "college premium" was at 81% -- employers prefer workers with more human capital (which going to college usually signals to firms)
Racial and gender discrimination can be seen as causes
Sometimes, bad luck (wage-earner loses job of falls ill) might be the reason for poverty
Economic Inequality
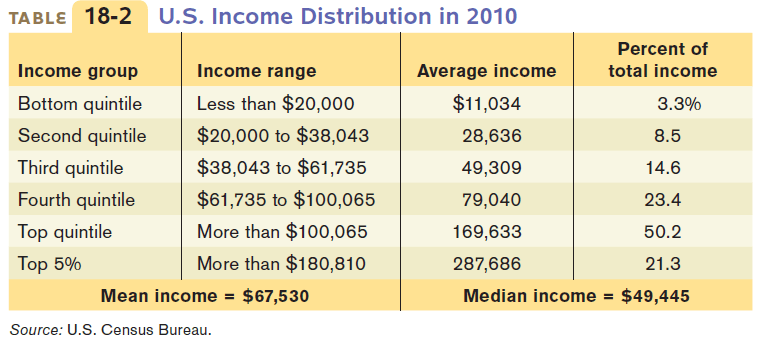
In 2008, the average US household income was $60,000
More precisely, the mean income was $68,424 while the median income was $50,303
The ultra-high salaries of the few (Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg) will make the mean greater than the median
Income is unequally distributed as data from the U.S. Census Bureau shows
Gini Coefficient
The most widely used measure of inequality, it's a number that summarizes a country's level of inequality
High level of inequality (such as Brazil) would be 0.6 whereas in Sweden the number is at 0.25
The US has a relatively high Gini coefficient for such a wealthy country. In 2009, the number was at 0.468
High Gini levels appear in Africa and South America
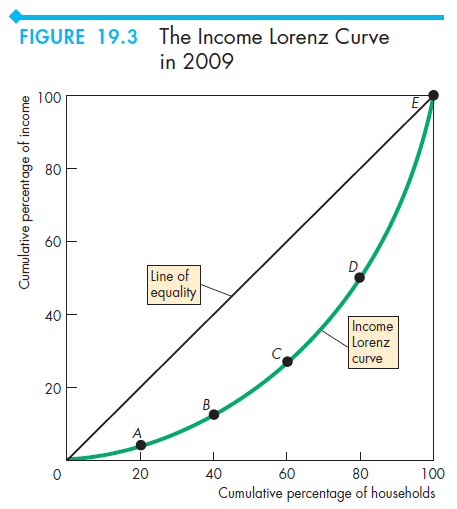
Lorenz Curve
a graph on which the cumulative percentage of total national income (or some other variable) is plotted against the cumulative percentage of the corresponding population (ranked in increasing size of share).
The extent to which the curve sags below a straight diagonal line indicates the degree of inequality of distribution.
Three Types of Taxes
Proportional Tax
- "flat" tax that takes a percentage of income regardless of the amount of income (ie. Hong Kong)
Regressive Tax
- tax rate decreases as the amount subject to taxation increases that imposes a greater burden on the poor than the rich (ie. payroll taxes or cigarette taxes)
Progressive Tax
- tax rate that goes up as income increases. Most conutries (including the US) have increasingly higher tax brackets for the wealthy
Means-Tested Programs
Welfare refers to money given to those that fall below the poverty threshold
In the US, Temporary Aid for Needy Families (TANF) assists families with children for a limited period of time
Replace the more controversial Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) which created perverse incentives for the poor
Supplemental Security Income help disabled individuals and Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program help low-income families with food
Negative income tax -- program that creates incentive for low-wage earners to make more money (Earned Income Tax Credit)
Food Stamps and Medicaid
Social Security and Unemployment
Largest US welfare program is Social Security
Retirement income for elderly, disable and provides "survivor benefits"
Wages subject to tax up maximum amount ($106,800 in 2010)
Unemployment insurance pays 35% of salary until a new job is found for a period of time (extended during recessions)
Financed through a tax on employers
Trade-offs exist between efficiency and equity, which is ultimately a normative issue